ArrayList
- ArrayList 的数据结构基于数组实现,这个数组不像普通定义的数组,它可以在 ArrayList 的管理下插入数据时按需动态扩容、进行数据拷贝等
- Array + List = 数组 + 列表 = ArrayList = 数组列表
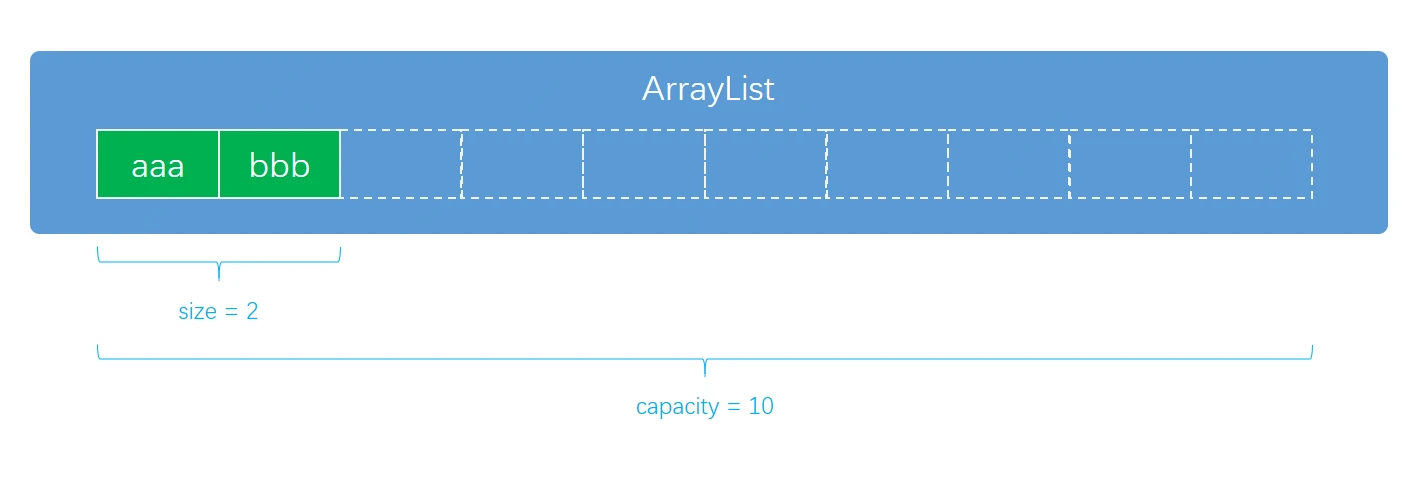
初始化
通常情况空构造函数初始化 ArrayList 更常用,这种方式数组的长度会在第一次插入数据时进行设置
当我们已经知道要填充到 ArrayList 中的元素个数时,为了提高性能,减少 ArrayList 中的拷贝操作,我们会直接初始化一个预先设定好的长度
EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 是一个定义好的空对象,
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}初始化方式:
- 普通方式:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("ccc"); - 内部类方式:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>() {
add("aaa");
add("bbb");
add("ccc");
}; - Arrays.asList:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList("aaa", "bbb", "ccc")); - Collections.nCopies
Collections.nCopies 是集合方法中用于生成多少分指定元素的方法ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(Collections.nCopies(10, 0));
- 普通方式:
ArrayList 构造函数:
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}- 实现 Collectio 接口的类都可以作为入参传递
- 入参通过转为数组及拷贝
Arrays.copyOf到Object[]集合中赋值给属性elementData
Arrays.asList:
- 使用 Arrays.List 构建的集合不能赋值给 ArrayList
- 使用 Arrays.List 构建的集合不能添加、删除元素
- 原因: Arrays.asList 构造出来的 List 和 new ArrayList 得到的 List 不是同一个类的对象,Arrays 下的 List 是一个私有类,只能通过 asList 使用,不能单独创建,这个 ArrayList 不能添加和删除,主要是因为它的实现方式,可以参考 Arrays 类中,这部分源码,
private static class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess, java.io.Serializable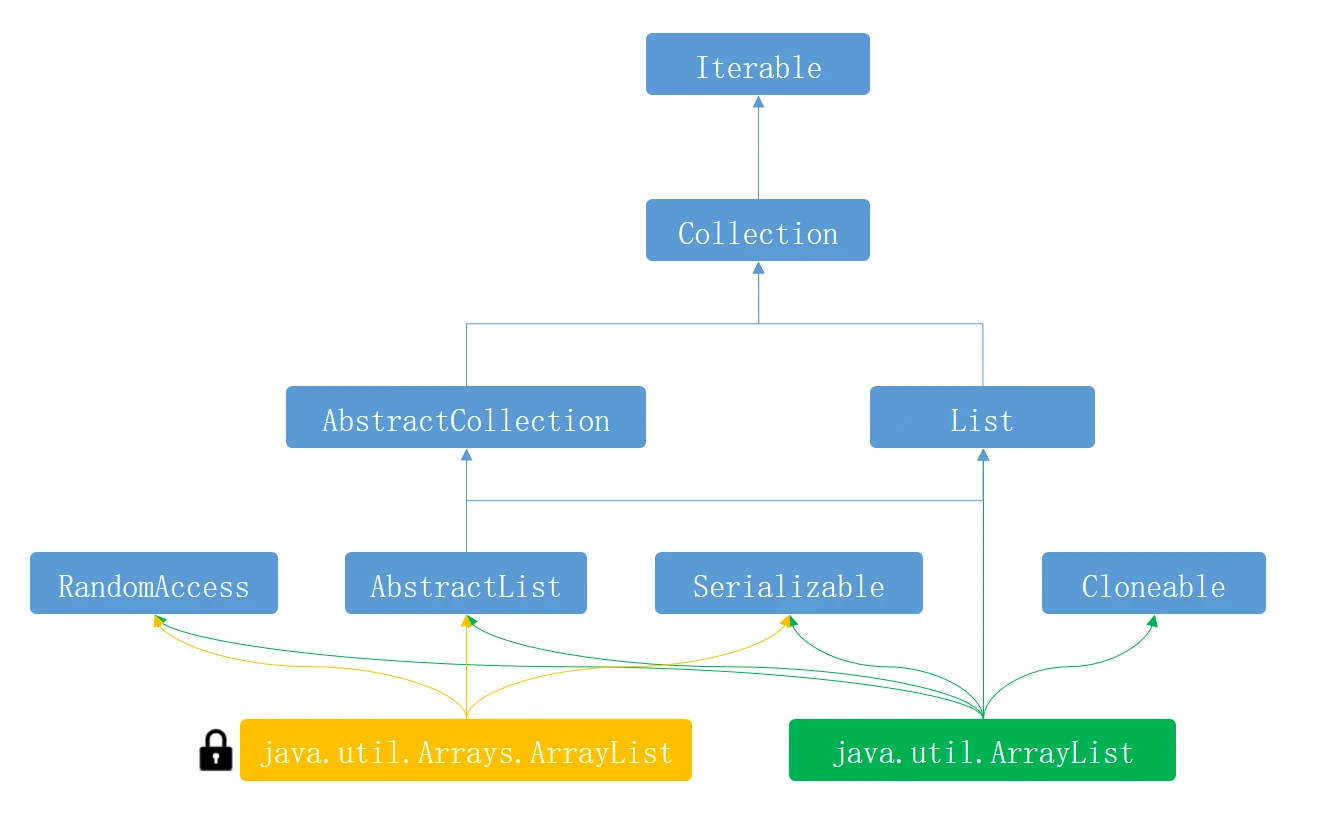
插入
ArrayList 对元素的插入,其实就是对数组的操作,只不过在特定时候需要扩容
普通插入:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("ccc");源码: 插入元素时size++自增,把对应元素添加进去
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}指定位置插入:
list.add(2, "1");插入时扩容:
- ArrayList默认初始化时会申请10个长度的空间,如果超过这个长度则需要进行扩容,申请新的数组长度,并把原数组元素拷贝到新数组中
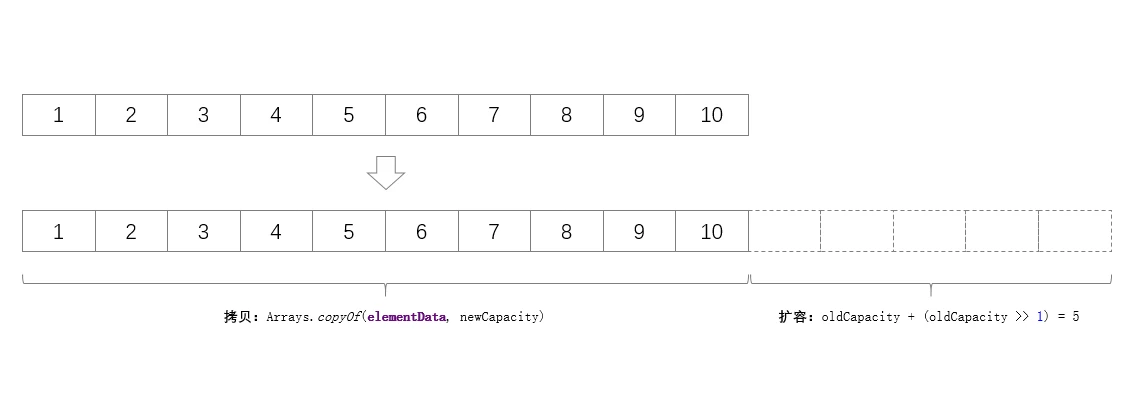
- 判断长度充足时,
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1) - 判断长度不足时,通过扩大函数,进行扩容,
grow(int minCapacity) - 扩容的长度计算: 旧容量 + 旧容量右移一位(
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);),这相当于扩容为原来容量的(int)3/2,扩容时:0111 + 0111 >> 1 = 0111 + 0011 = 7 + 3 = 10 - 扩容完成后,需要把原数组中的数据拷贝到新数组中,过程会使用到
Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity),但底层实现是System.arrayCopy
- 判断长度充足时,
- ArrayList默认初始化时会申请10个长度的空间,如果超过这个长度则需要进行扩容,申请新的数组长度,并把原数组元素拷贝到新数组中
元素迁移:

- 判断size,是否可以进行插入
- 判断插入后是否需要进行扩容,
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); - 数据元素迁移,把从待插入位置后面的元素顺序向后迁移
- 给数组的指定位置赋值,即插入元素
部分源码:
public void add(int index, E element) {
...
// 判断是否需要扩容以及扩容操作
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
// 数据拷贝迁移,把待插入位置空出来
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
// 数据插入操作
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
删除
- 删除:
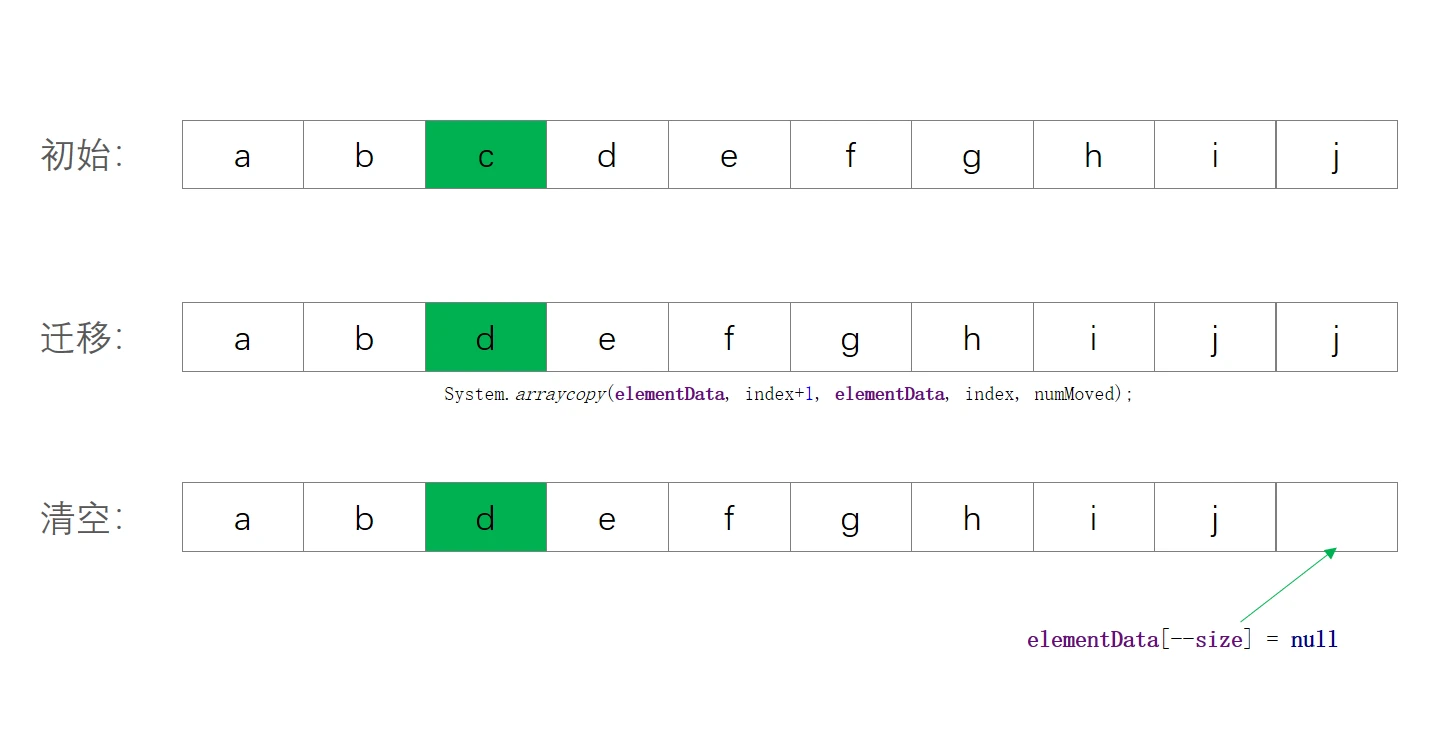
- 过程:
- 校验是否越界,
rangeCheck(index) - 计算删除元素的移动长度
numMoved,通过System.arrayCopy将元素复制给自身 - 清空结尾元素,
elementData[--size] = null
- 校验是否越界,
- 过程: