StringBuilder和String
String、StringBuilder、StringBuffer字符串链接性能对比: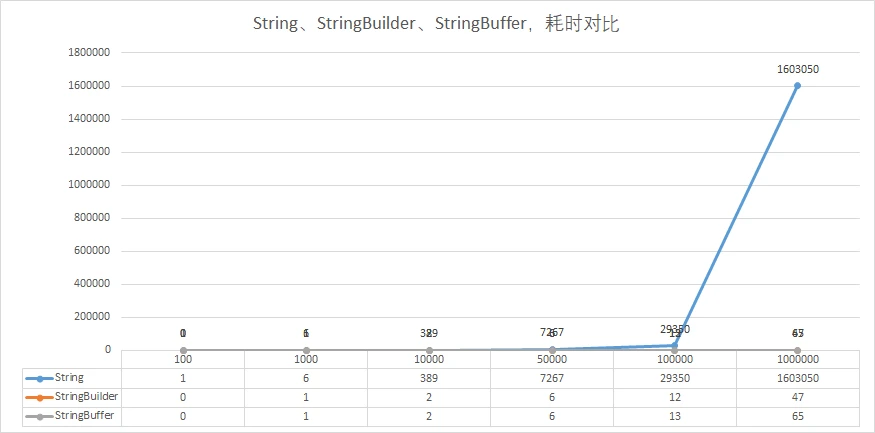
String字符串链接最为耗时,数据量大时极其明显StringBuilder、StringBuffer因为没有发生多线程竞争,因此没有锁升级,所以耗时基本相同,单线程下更推荐StringBuffer
String 源码
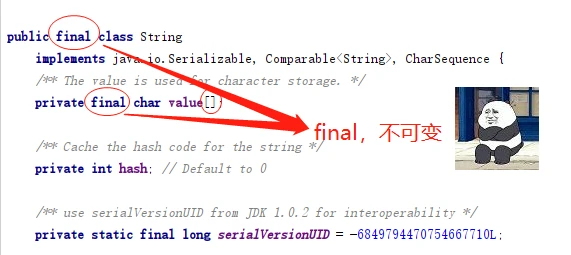
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0
/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6849794470754667710L;
...
}
初始化
初始化方式:
String str_01 = "abc";
System.out.println("默认方式:" + str_01);
String str_02 = new String(new char[]{'a', 'b', 'c'});
System.out.println("char方式:" + str_02);
String str_03 = new String(new int[]{0x61, 0x62, 0x63}, 0, 3);
System.out.println("int方式:" + str_03);
String str_04 = new String(new byte[]{0x61, 0x62, 0x63});
System.out.println("byte方式:" + str_04);源码:
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return value[index];
}以O(1)的时间复杂度从数组中获取元素,效率很高
不可变(final)
例子:
String str_01 = "abc";
String str_02 = "abc" + "def";
String str_03 = str_01 + "def";
// 反编译后的字节码:
public void test_00();
Code:
0: ldc #2 // String abc
2: astore_1
3: ldc #3 // String abcdef
5: astore_2
6: new #4 // class java/lang/StringBuilder
9: dup
10: invokespecial #5 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder."<init>":()V
13: aload_1
14: invokevirtual #6 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
17: ldc #7 // String def
19: invokevirtual #6 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
22: invokevirtual #8 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
25: astore_3
26: return- str_01 = "abc",指令码:0: ldc,创建了一个对象
- str_02 = "abc" + "def",指令码:3: ldc // String abcdef,得益于JVM编译期的优化,两个字符串会进行相连,创建一个对象存储
- str_03 = str_01 + "def",指令码:invokevirtual,这个就不一样了,它需要把两个字符串相连,会创建StringBuilder对象,直至最后toString:()操作,共创建了三个对象
- 字符串的,操作是不可修改的,相连操作会创建出新对象
intern()
源码:
/**
* Returns a canonical representation for the string object.
* <p>
* A pool of strings, initially empty, is maintained privately by the
* class {@code String}.
* <p>
* When the intern method is invoked, if the pool already contains a
* string equal to this {@code String} object as determined by
* the {@link #equals(Object)} method, then the string from the pool is
* returned. Otherwise, this {@code String} object is added to the
* pool and a reference to this {@code String} object is returned.
* <p>
* It follows that for any two strings {@code s} and {@code t},
* {@code s.intern() == t.intern()} is {@code true}
* if and only if {@code s.equals(t)} is {@code true}.
* <p>
* All literal strings and string-valued constant expressions are
* interned. String literals are defined in section 3.10.5 of the
* <cite>The Java™ Language Specification</cite>.
*
* @return a string that has the same contents as this string, but is
* guaranteed to be from a pool of unique strings.
*/
public native String intern();native代表intern()是一个本地方法,底层通过JNI调用C++编写的功能
\openjdk8\jdk\src\share\native\java\lang\String.c:Java_java_lang_String_intern(JNIEnv *env, jobject this)
{
return JVM_InternString(env, this);
}
oop result = StringTable::intern(string, CHECK_NULL);
oop StringTable::intern(Handle string_or_null, jchar* name,
int len, TRAPS) {
unsigned int hashValue = java_lang_String::hash_string(name, len);
int index = the_table()->hash_to_index(hashValue);
oop string = the_table()->lookup(index, name, len, hashValue);
if (string != NULL) return string;
return the_table()->basic_add(index, string_or_null, name, len,
hashValue, CHECK_NULL);
}图解:
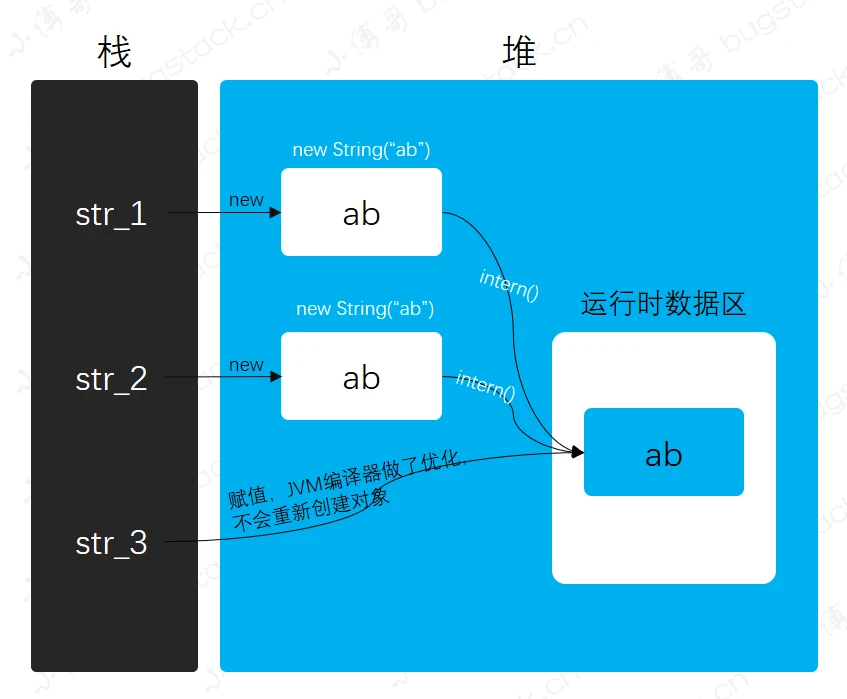
==: 基础类型进行值比较,引用类型进行地址比较,equal进行哈希值比较- 两个
new出来的对象地址不同,所以不相等 intern()直接把值推进常量池,两个对象做intern()操作后,比对的是常量池里的值str_3 = "ab"赋值中,JVM编译器做了优化,不会重新创建对象,直接引用常量池里的值,因此str_1.intern() == str_3结果为true
StringBuilder 源码
初始化
传入初始化容量、传入字符串
new StringBuilder();
new StringBuilder(16);
new StringBuilder("abc");源码:
public StringBuilder() {
super(16);
}
AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) {
value = new char[capacity];
}
添加元素
使用
appendstringBuilder.append("a");
stringBuilder.append("b");
stringBuilder.append("c");入口方法
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
if (str == null)
return appendNull();
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}StringBUffer继承自AbstractStringBUilder,共用这个方法- 这个方法包括了容量检测、元素拷贝、记录
count数量
扩容操作
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);/**
* This method has the same contract as ensureCapacity, but is
* never synchronized.
*/
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0)
expandCapacity(minimumCapacity);
}
/**
* This implements the expansion semantics of ensureCapacity with no
* size check or synchronization.
*/
void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2;
if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minimumCapacity;
if (newCapacity < 0) {
if (minimumCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity);
}原理与操作数组相同,需要检测容量大小,按需扩容,扩容容量为
n * 2 + 2, 然后进行元素拷贝填充元素
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin) {
// ...
System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
}基于本地方法
System.arraycopy实现toString()
stringBuilder.toString();@Override
public String toString() {
// Create a copy, don't share the array
return new String(value, 0, count);
}使用
String的构造函数传递数组进行转换
StringBuffer 源码
StringBuffer和StringBuilderAPI的使用和底层实现基本一致,不同的是StringBuffer加了synchronized锁,因此是线程安全的为了减少获取锁和释放锁带来的性能损耗,JVM引入了偏向锁、轻量级锁、重量级锁来进行优化,锁升级如下图:@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer append(String str) {
toStringCache = null;
super.append(str);
return this;
}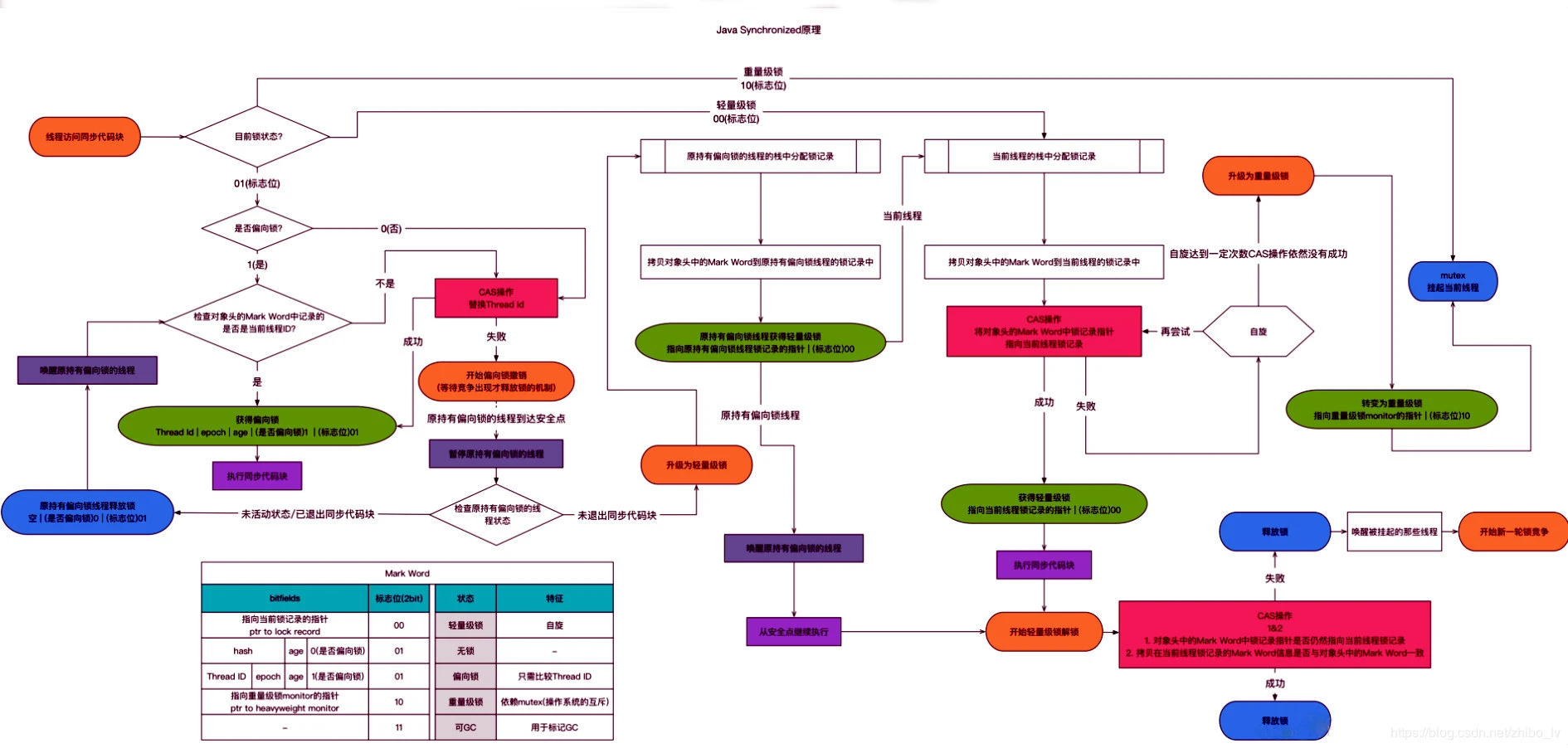
- 从无锁状态开始,当线程进入
synchronized同步代码块,会检查对象头和栈帧内是否有当先线程ID编号,无则使用CAS替换 - 解锁时,会使用
CAS将Displaced Mark Word替换回对象头,如果成功则表示竞争没有发生,反之则表示当前锁存在竞争,锁就会升级成重量级锁 - 大多数情况下锁是不发生竞争的,基本由一个线程持有,所以为了避免获得锁和释放锁带来的性能损耗,引入锁升级,升级后不能降级
- 从无锁状态开始,当线程进入