ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal主要解决线程内资源共享问题,一般会用在全链路监控中
应用场景
SimpleDateFormat
demo
private SimpleDateFormat f = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public void seckillSku(){
String dateStr = f.format(new Date());
// 业务流程
}SimpleDateFormat不是一个线程安全的类使用
ThreadLocal优化private static ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
new Thread(() -> {
String dateStr = threadLocal.get().format(new Date());
try {
Date parseDate = threadLocal.get().parse(dateStr);
String dateStrCheck = threadLocal.get().format(parseDate);
boolean equals = dateStr.equals(dateStrCheck);
if (!equals) {
System.out.println(equals + " " + dateStr + " " + dateStrCheck);
} else {
System.out.println(equals);
}
} catch (ParseException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}).start();
}
}把
SimpleDateFormat放在ThreadLocal中使用,不需要重复new,同时避免线程不安全问题
链路追踪
- 基于谷歌
Dapper论文实现的非侵入全链路追踪,不需要使用硬编码的方式进行监控,采用JavaAgent+ 字节码插桩的方式动态采集方法执行信息 - 在动态采集方法执行信息中,字节码插桩解决的是非侵入式编程,在一次服务调用中,在各个系统以及系统内多个方法的调用都需要进行采集,这个时候就需要使用
ThreadLocal记录方法执行ID,同时存在跨线程调用(使用增强版本的ThreadLocal) - 字节码插桩使用
byte-buddy,实际上就是使用ASM或者Javassist - 具体案例和代码: 基于JavaAgent的全链路监控一《嗨!JavaAgent》
数据结构
ThreadLocal的简单使用:new ThreadLocal<String>().set("字符串");- 部分源码:
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
...
}ThreadLocal底层采用数组结构存储数据,使用哈希值计算下标,是一个散列表的数据结构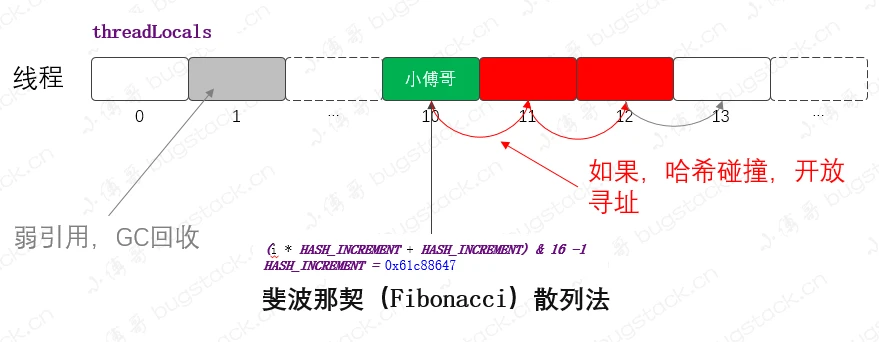
- 数组结构
Entry: 是一个弱引用实现,static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>>,表明只要没有强引用存在,发生GC时就会被垃圾回收- 数据元素采用哈希散列的方式进行存储,使用
斐波那契散列法 - 不同于
HashMap的数据结构,发生哈希碰撞不会存储成链表或者红黑树,而是使用拉链法进行存储,即当同一个下标位置发生冲突时,+1向后寻址,直到找到空位或者垃圾回收位置进行存储
散列算法
ThreadLocal计算哈希值代码:private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}- 计算哈希的方式: 除数散列法、平方散列法、斐波那契散列法、随机数法
ThreadLocal使用斐波那契散列法是为了让数据更加散列,减少哈希碰撞,具体来自数学公式的计算求值:f(k) = ((k * 2654435769) >> X) << Y对于常见的32位整数而言,也就是f(k) = (k * 2654435769) >> 28- 数字
0x61c88647: 哈希值的黄金分割点(0.618),计算公式:(√5 - 1) / 2,取10位近似 0.6180339887,之后使用// 黄金分割点:(√5 - 1) / 2 = 0.6180339887
// 1.618:1 == 1:0.618
System.out.println(BigDecimal.valueOf(Math.pow(2, 32) * 0.6180339887).intValue()); //-16405315272 ^ 32 * 0.6180339887,得到结果-1640531527,等于16进制的0x61c88647
源码
初始化
new ThreadLocal<>(): 可以根据自己需要的泛型进行设置哈希值的获取:
threadLocalHashCode,私有变量,通过getClass().getDeclaredField("threadLocalHashCode")获取private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
/**
* Returns the next hash code.
*/
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
设置元素
new ThreadLocal<>().set("字符串");
流程图: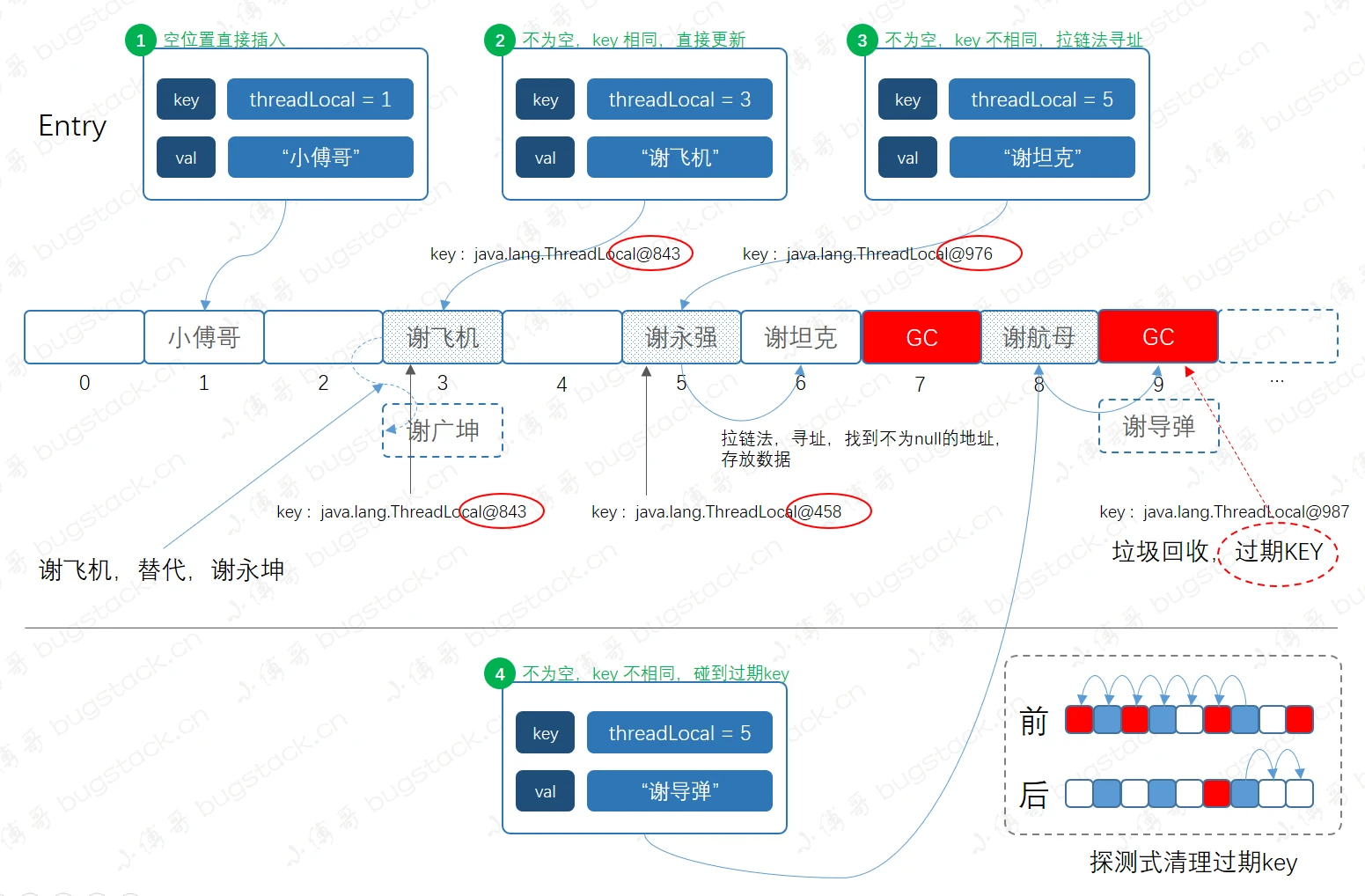
元素插入时通过斐波那契散列法计算下标值进行存放,分为四种情况- 待插入的下标位置为空,直接插入
- 待插入的下标位置不为空,key相同,直接替换
- 待插入的下标位置不为空,key不同,使用拉链法寻址
- 待插入的下标位置不为空,key过期(弱引用发生GC时的情况),
ThreadLocal会进行探测清理过期key
- 源码
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);: 斐波那契散列,计算数组下标Entry: 弱引用对象的实现类,static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>>,在没有外部强引用时会被GC回收删除key- for循环判断元素是否存在,当前下标位置不存在元素时直接设置元素,
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); - 如果元素存在则会判断key是否相同,
if ( k == key ),相等则更新值 - 不相等则使用
replaceStaleEntry,探测式清理过期元素
扩容机制
扩容条件
// 判断是否扩容
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();- 进行启发式清理
cleanSomeSlots,清理过期元素 - 判断
sz >= threshold,其中threshold = len * 2 / 3,即数组中元素大于len * 2 / 3时就需要进行扩容 - 最后,rehash(),扩容重新计算元素位置
- 进行启发式清理
源码
探测式清理过期元素,并判断清理后是否满足扩容条件,
size >= threshold * 3 / 4,满足后执行扩容操作,重新计算哈希值并把元素拷贝到新数组中private void rehash() {
expungeStaleEntries();
// Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
resize();
}
private void expungeStaleEntries() {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = tab[j];
if (e != null && e.get() == null)
expungeStaleEntry(j);
}
}resize()源码private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null; // Help the GC
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
table = newTab;
}
步骤:
- 首先把数组长度扩容到原来的2倍,
oldLen * 2,实例化新数组 - for遍历,进行元素拷贝,把所有旧数组中的元素放到新数组中
- 拷贝过程中,发生哈希碰撞则使用拉链法顺延
- 过程中对key值进行检测,
if ( k == null ),方便GC
- 首先把数组长度扩容到原来的2倍,
获取元素
new ThreadLocal<>().get();

- 直接定位到,没有哈希冲突,直接返回元素
- 没有直接定位到,key不同,进行拉链式查找
- 没有直接定位到,key不同,拉链式查找,遇到GC清理元素则需要探测式清理,再寻找元素
源码:
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
元素清理
- 探测式清理(
expungeStaleEntry): 以当前遇到的GC元素开始,向后不断清理,直到遇到null为止才停止rehash计算探测式清理在获取元素中使用到,private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// expunge entry at staleSlot
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}new ThreadLocal<>().get() -> map.getEntry(this) -> getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e) -> expungeStaleEntry(i) - 启发式清理(
cleanSomeSlots): 试探性扫描一些单元格寻找过期元素(被垃圾回收的元素),当添加新元素或者删除另一个过期元素时将调用此函数。它执行对数扫描次数,作为不扫描(快速但保留垃圾)和与元素数量成比例的扫描次数之间的平衡点,这能找到所有垃圾,但是会导致一些插入花费O(n)的时间while循环中不断右移寻找需要被清理的过期元素,最终都会使用private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);
return removed;
}expungeStaleEntry进行处理,这其中还包括元素的移位