队列
被抛弃的Stack

peek: 意为偷看,即查看一下,并不会弹出元素,满足后进先出的规则,查看到的是最后放进去的元素
lastElement、firstElement: 获取最后一个/第一个元素
pop: 从队列中弹出元素,弹出后也就意味着把属于这个位置的元素清空删除
源码:
/**
*
* <p>A more complete and consistent set of LIFO stack operations is
* provided by the {@link Deque} interface and its implementations, which
* should be used in preference to this class. For example:
* <pre> {@code
* Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();}</pre>
*
* @author Jonathan Payne
* @since JDK1.0
*/
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E>s.push("aaa");
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}- Stack栈是在JDK1.0时代基于继承Vector实现的,本身Vector就是一个不推荐使用的类,主要在于他的一些操作方法锁(synchronized)的粒度太粗,都是放到方法上的
- Stack栈底层使用Vector数组实现,数组结构在元素添加时需要通过
System.arrayCopy进行扩容操作,而栈本身的特点是首尾元素的操作,不需要遍历,使用数组结构并不理想 - 这个方法的注释上明确标出推荐使用
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();,虽然同样是数组结构,但是没有粗粒度的锁,同时可以申请指定空间并且在扩容时操作也优于Stack,并且是一个双端队列,使用起来更加灵活
双端队列 ArrayDeque
ArrayDeque是基于数组实现的可动态扩容的双端队列,可以在队列的头和尾同时插入和弹出元素,当元素数量超过数组初始化长度是,则需要扩容并迁移数据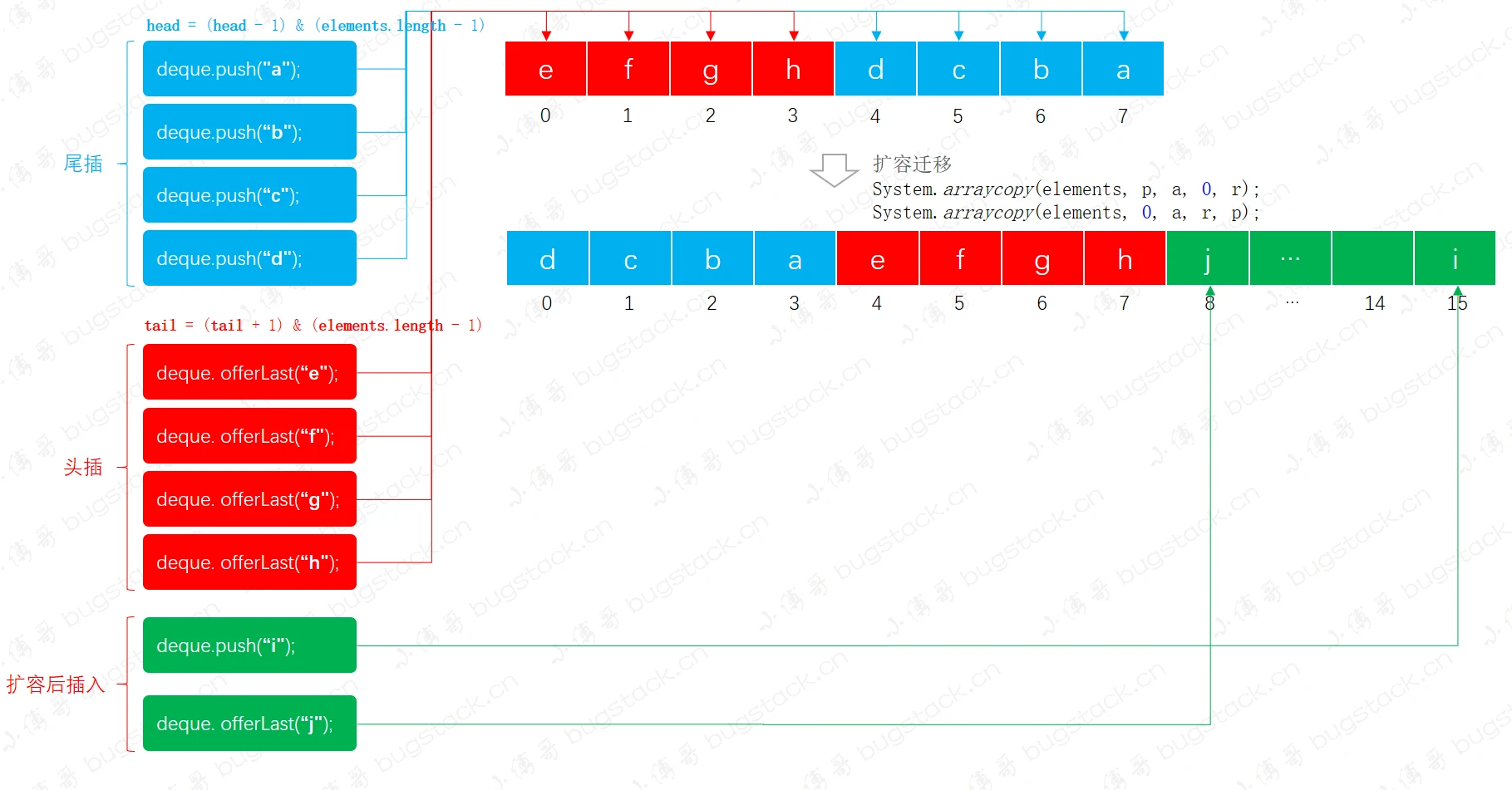
- 双端队列基于数组实现,所以需要扩容、迁移数据等操作
- push、offerFirst、addFirst几个操作效果一致,向头部插入,offerLast、addLast是向尾部插入,这样两端都满足后进先出
- 双端队列就是一个环形,所以扩容后继续插入元素也满足后进先出
源码
初始化
new ArrayDeque<String>(1)构造函数初始化提供多个方法,可以指定大小、提供默认元素,在初始化时与HashMap相似,需要找到当前传输值最小的2的幂次方作为容量private static int calculateSize(int numElements) {
int initialCapacity = MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
// Find the best power of two to hold elements.
// Tests "<=" because arrays aren't kept full.
if (numElements >= initialCapacity) {
initialCapacity = numElements;
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 1);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 2);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 4);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 8);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 16);
initialCapacity++;
if (initialCapacity < 0) // Too many elements, must back off
initialCapacity >>>= 1;// Good luck allocating 2 ^ 30 element
}
return initialCapacity;
}
入栈
deque.push("a");ArrayDeque提供一个push方法,与deque.offerFirst("a")等价,底层源码相同// addFirst
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e;
if (head == tail)
doubleCapacity();
}
// addLast
public void addLast(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[tail] = e;
if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}- addFirst(): 定位下标,
head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1),因为数组长度为2^n的倍数,因此2^n-1就是一个全是1的二进制数,可以用于运算得出数组下标 - addLast(): 使用同样的方式定位下标,只不过从0开始,往上增加
- 当头(head)=尾(tail)时,则需要双倍扩容,doubleCapacity
- addFirst(): 定位下标,
双倍扩容,数据迁移
- 源码: 进行两倍扩容
private void doubleCapacity() {
assert head == tail;
int p = head;
int n = elements.length;
int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
int newCapacity = n << 1;
if (newCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
elements = a;
head = 0;
tail = n;
}n << 1, 同时把两端数据迁移进新的数组 - 过程:
- head和tail相等时进行扩容操作
- 进行数据迁移,使用
System.arrayCopy - 添加新元素
双端队列 LinkedList
- 数据结构:
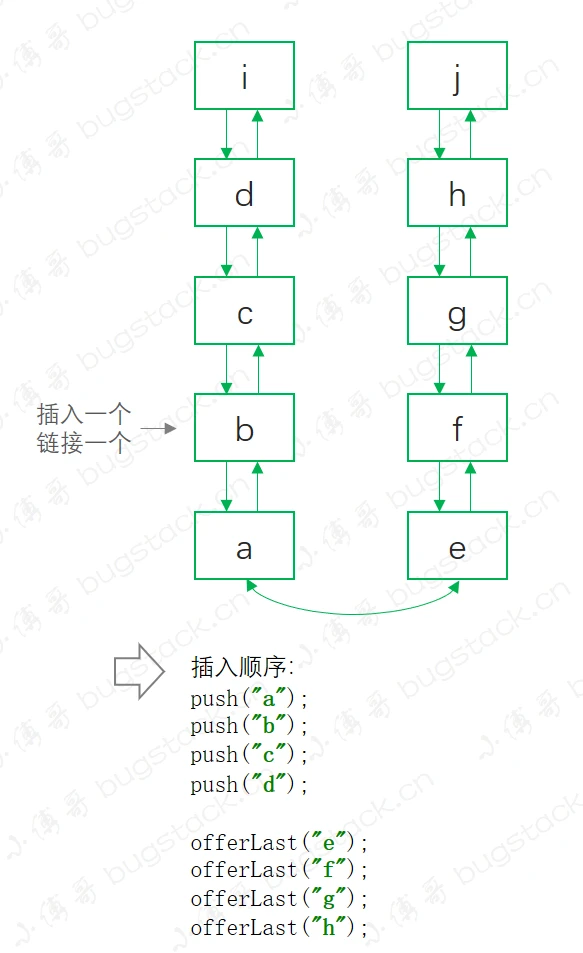
- LinkedList天生支持双端队列,从头、尾取数据时间复杂度均为O(1),数据的插入和删除也不需要进行扩容拷贝数据
源码
压栈:
// deque.push("a");、deque.offerFirst("a")
deque.push("a");、deque.offerFirst("a")private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// deque.offerLast("e");
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}linkFirst、linkLast: 分别是给链表的首尾节点插入元素,因为是链表结构,因此不需要进行扩容,只需要把双向链路连接上即可
延时队列 DelayQueue
可以通过设定时间,依次轮询获取
实现类模板:
public class TestDelayed implements Delayed {
private String str;
private long time;
public TestDelayed(String str, long time, TimeUnit unit) {
this.str = str;
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis() + (time > 0 ? unit.toMillis(time) : 0);
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return time - System.currentTimeMillis();
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
TestDelayed work = (TestDelayed) o;
long diff = this.time - work.time;
if (diff <= 0) {
return -1;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
public String getStr() {
return str;
}
}
源码
元素入栈:
delayQueue.offer(new TestDelayed("aaa", 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS));public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e;
else
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
private void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = queue[parent];
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = x;
}- 基于是数组实现,可以进行动态扩容,插入元素的顺序并不影响最终的输出顺序
- 元素的排序依赖于compareTo方法进行,即由休眠时间长短决定
- 只有实现了Delayed接口,才能存放元素
元素出栈
delayQueue.take()public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
E first = q.peek();
if (first == null)
available.await();
else {
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS
if (delay <= 0)
return q.poll();
first = null; // don't retain ref while
if (leader != null)
available.await();
else {
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentT
leader = thisThread;
try {
available.awaitNanos(delay);
} finally {
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
if (leader == null && q.peek() != null)
available.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}DelayQueue是Leader-Followr模式的变种,消费者线程处于等待await时,总是等待最先休眠完成的元素
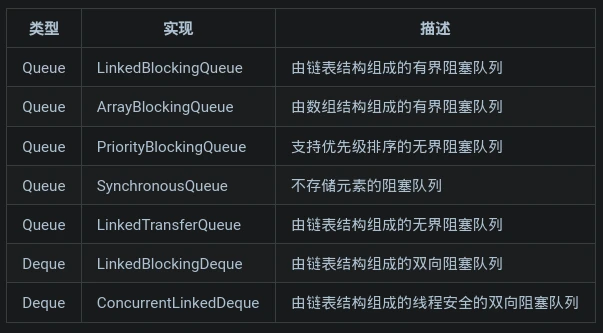
其他队列
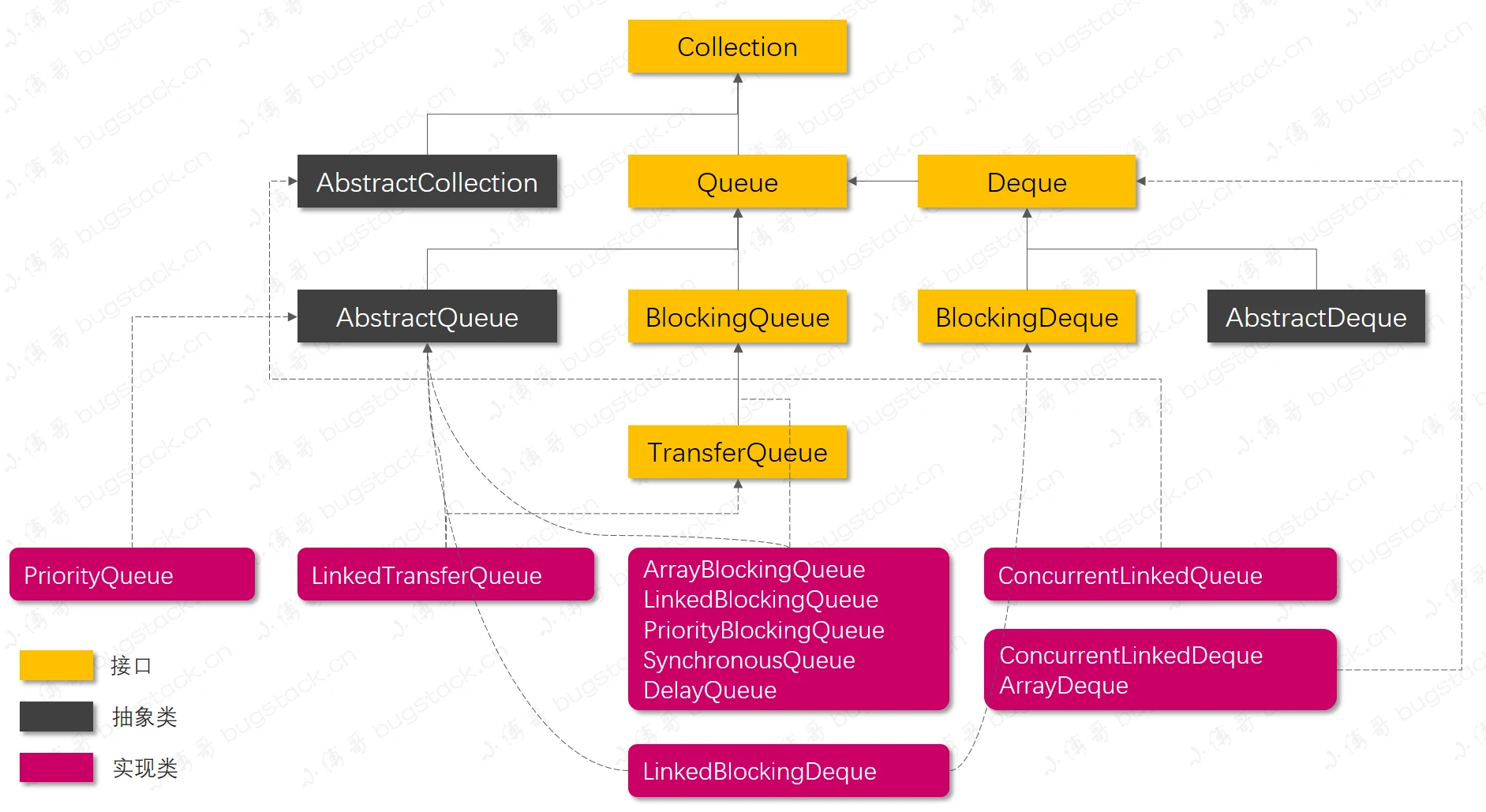
- 队列类结构: